Field results: Improvements with immune-complex vaccine (Part 2)
Introduction:
GUMBOHATCH® is a new immune-complex vaccine against Infectious bursal disease (IBD) developed by HIPRA (Spain). This new immune-complex vaccine has introduced a different formulation (IgY of egg origin) and control parameters (free IgY detection and neutralization control) to ensure the complete coating of the IBDV virus.
All these new improvements have resulted in a newly formulated immune-complex vaccine, which ensures the maintenance of the maximum potency of the vaccine and consistent results in the field, even in the presence of high levels of maternal antibodies1.
The aim of this multicentre, positive-controlled and blind clinical trial was to evaluate the safety and efficacy of GUMBOHATCH® (immune-complex vaccine against Infectious bursal disease) when administered via the in ovo route under field conditions compared with a standard formulated immune-complex vaccine in Brazil.
Methods:
A total of 112,100 chicks in a hatchery were vaccinated in ovo (18 days of incubation) with GUMBOHATCH® (n= 56,200) or with a commercial IBD-complex vaccine (n=55,900) as a reference for a standard formulated vaccine, following the manufacturer’s instructions.
After hatching, the chicks were distributed to 3 commercial broiler farms located in the Paraná state. On each farm the two groups were housed in separate units under identical conditions and monitored up to the end of rearing (40 days of life). Several safety and efficacy parameters were evaluated during this period.
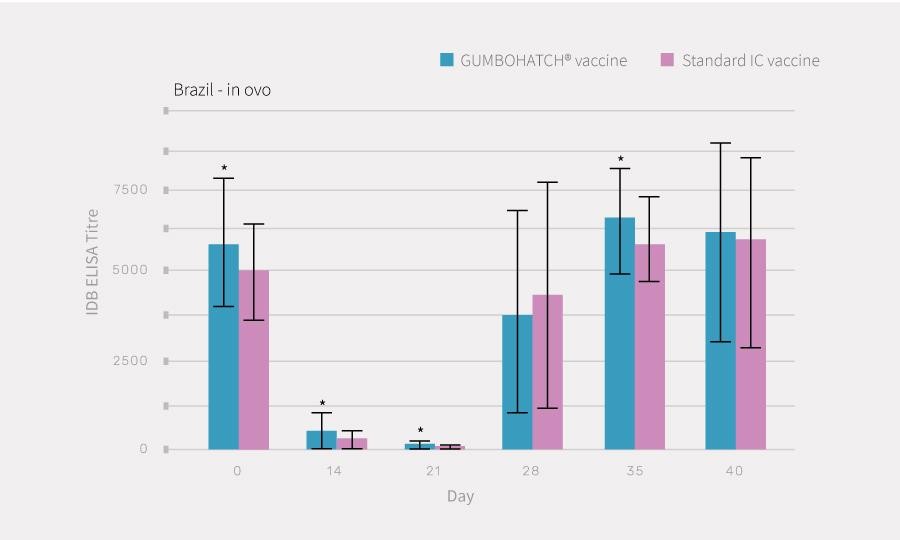
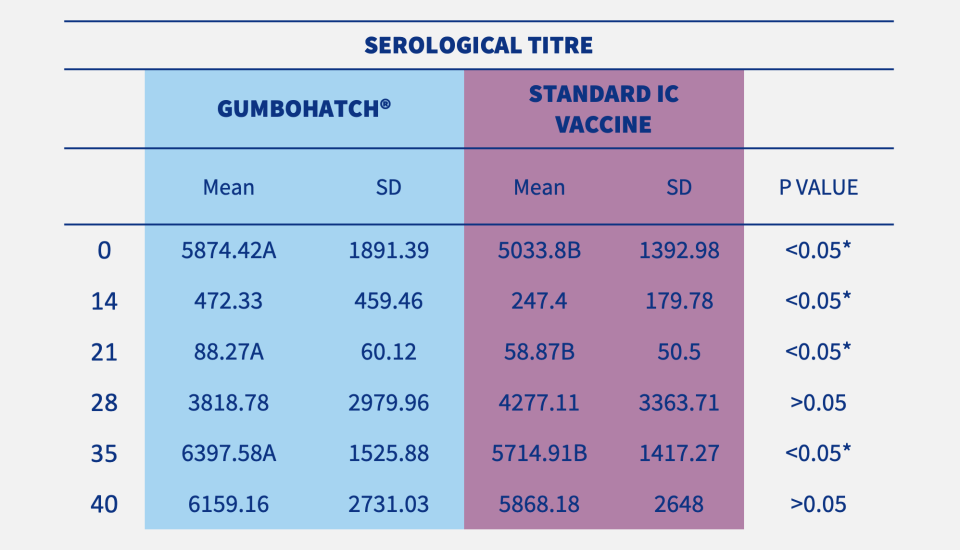
Blood sampling and necropsy of 15 chicks per group and farm were performed at different time points. Antibody titres to the IBD virus were determined using CIVTEST® AVI IBD (HIPRA). During necropsies, macroscopic bursal lesions were evaluated and bursal imprints were collected on FTA cards for PCR analysis. Data from the three farms were analysed altogether.
Results:
• SAFETY: No adverse reactions to either of the two vaccines were observed.
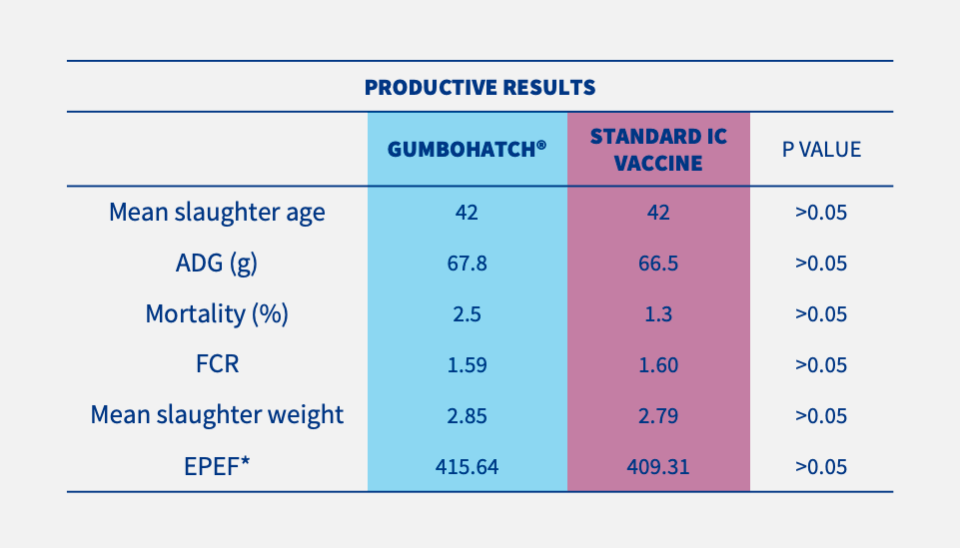
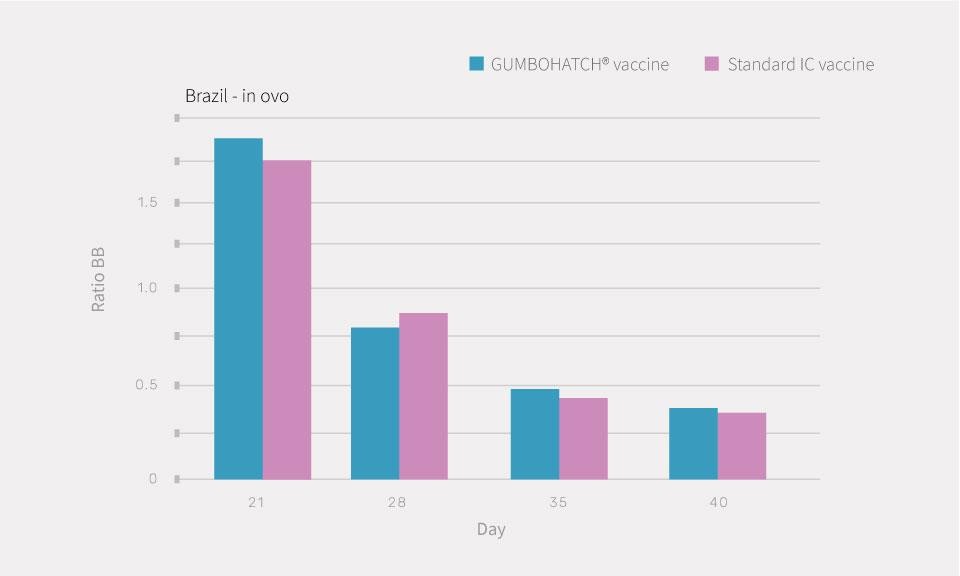
Similar hatchability, body weight after hatching, European Production Efficiency Factor and Ratio of Bursa-to-Body weight (BB ratio) were observed in both groups.
The overall incidence of bursal lesions was low and similar in both groups, although the incidence of petechial lesions in the GUMBOHATCH® group was significantly lower (p=0.04).
• EFFICACY: No clinical outbreak of IBD occurred on any farm. Similar results were observed in both groups in terms of performance parameters such as body weight gain and feed conversion rate (Table 1).