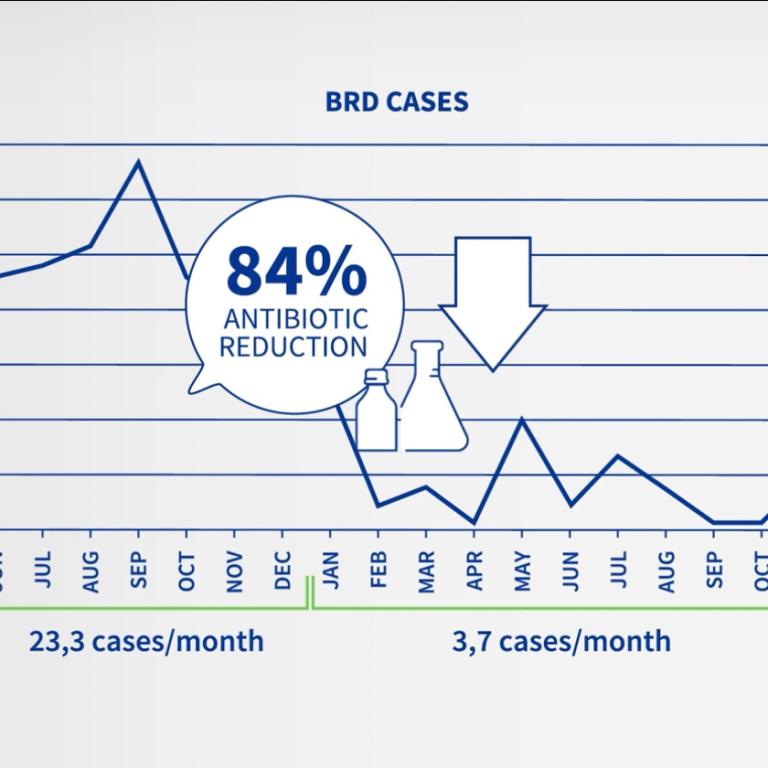
NEW FOREST EYE, PINKEYE, IBK
AETIOLOGY:
Moraxella bovis, Moraxella ovis and Moraxella bovoculi may act as main agents.
TRANSMISSION:
The infection becomes located in the lachrymal apparatus of the carrier cows. Mechanical corneal lesion, transmission by flies, mechanical vectors, etc.
CLINICAL SIGNS:
Epidemic outbreaks when it enters a farm for the first time; greater incidence in hot months (flies, dust, higher UV solar radiation, etc.) and, generally, affects younger animals, later developing into immunity in the adult herds. Generally unilateral, runs its course with blepharospasm, epiphora, conjunctivitis, photophobia, corneal infection and ulceration. In addition to the ocular lesion itself, IBK implies a diminution of milk production and of the conversion rate and growth of fattening calves.
LESIONS:
Tearing, eyes closed due to photophobia, corneal oedema (whitish cornea). Rounded ulceration in the central part of the cornea, which could be resolved with or without treatment, or by completing the ulceration of all of the corneal parenchymal. In some cases, continued active ulceration may cause corneal rupture. Relapse may occur at any stage of recovery.
DIAGNOSIS:
- Clinical: from the lesions. The differential diagnosis should include IBR and Listeriosis foreign bodies or parasites.
- Bacteriology: culture and antibiogram.
TREATMENT, PREVENTION AND CONTROL:
Topical, ocular or subconjunctival antibiotic treatment, depending on the severity of the case (whether or not corneal ulceration is present). Anti-inflammatories may be used, but corticosteroids should be avoided as long as there is ulceration. The antibiotics of choice are: penicillin, cephalosporin and tetracycline. Control dust, hygiene of the surroundings, correct spreading of the straw in the stables, fly control with insecticide.
Use of vaccines which includes the pili or adhesins involved. It is therefore, recommended that vaccinal control of IBR be established, since both problems (IBR and IBK) can co-exist and aggravate the presentation.